Heat generation and problem analysis
During the operation of the clutch assembly, power transmission is mainly achieved through the friction between the friction plate and the dual surface. Especially under high-speed operation, frequent starting or braking conditions, friction heat accumulates rapidly. If the heat cannot be effectively dissipated, the clutch temperature will rise rapidly, resulting in a "thermal decay" phenomenon, that is, the friction performance of the friction plate will decrease, affecting the transmission efficiency of the clutch, and may even cause problems such as aging of the friction material and overheating damage.
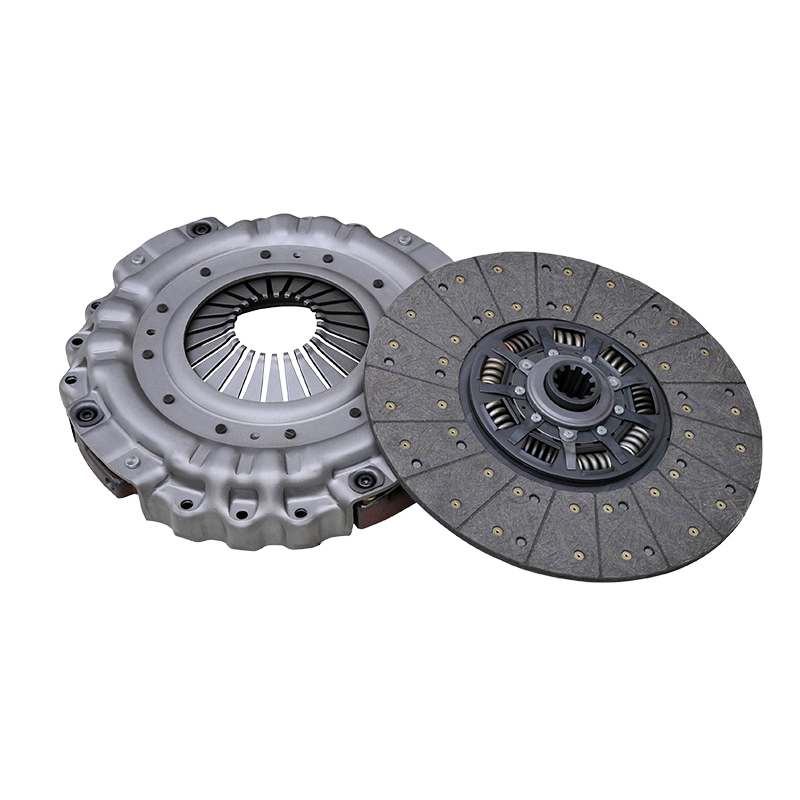
Application of high-performance composite friction plate materials
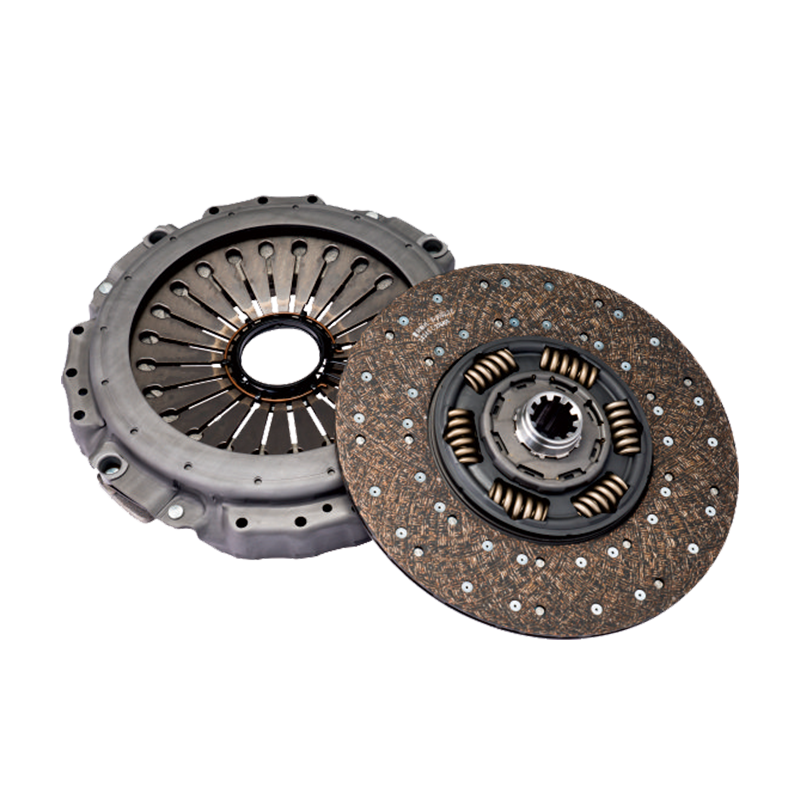
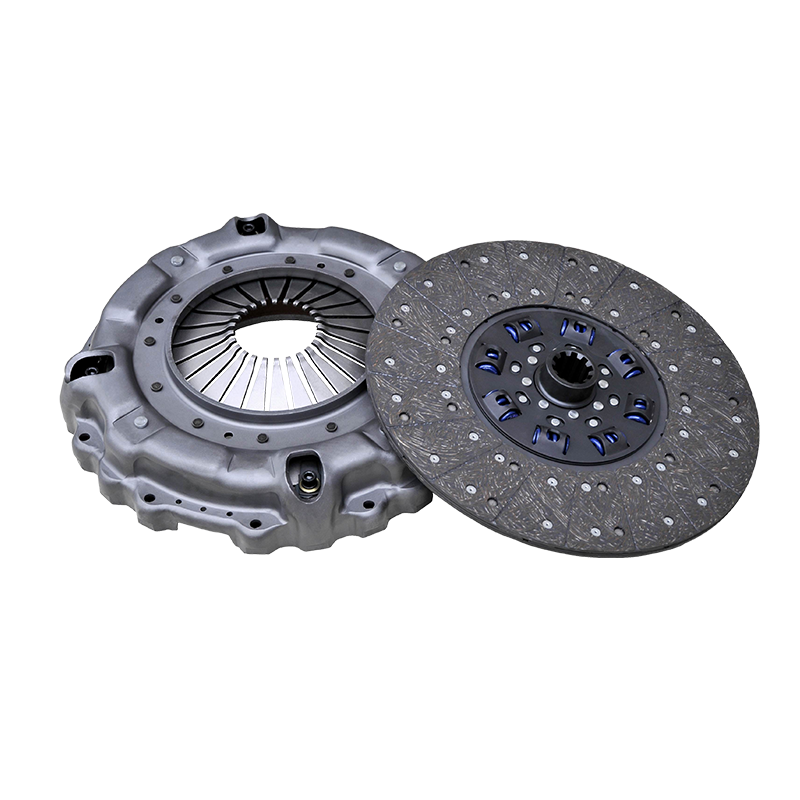
The high temperature resistance of the 430 push clutch assembly is due to its use of advanced friction plate materials. Clutch friction plates usually use high-temperature resistant composite materials, which have excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance. By quickly transferring the heat generated by friction, the composite material can effectively reduce the phenomenon of local heat accumulation. In addition, the high wear resistance of the composite material ensures that it can still maintain a long service life in a high temperature environment and is not prone to wear or damage.
This friction plate material is usually composed of a multi-layer composite structure, including carbon fiber, ceramic particles and metal powder, etc. These materials can not only withstand high temperatures, but also maintain a stable friction coefficient in high temperature environments, thereby effectively preventing the friction from decreasing at high temperatures and ensuring the stability and reliability of the clutch.
Optimized heat dissipation design and air cooling device
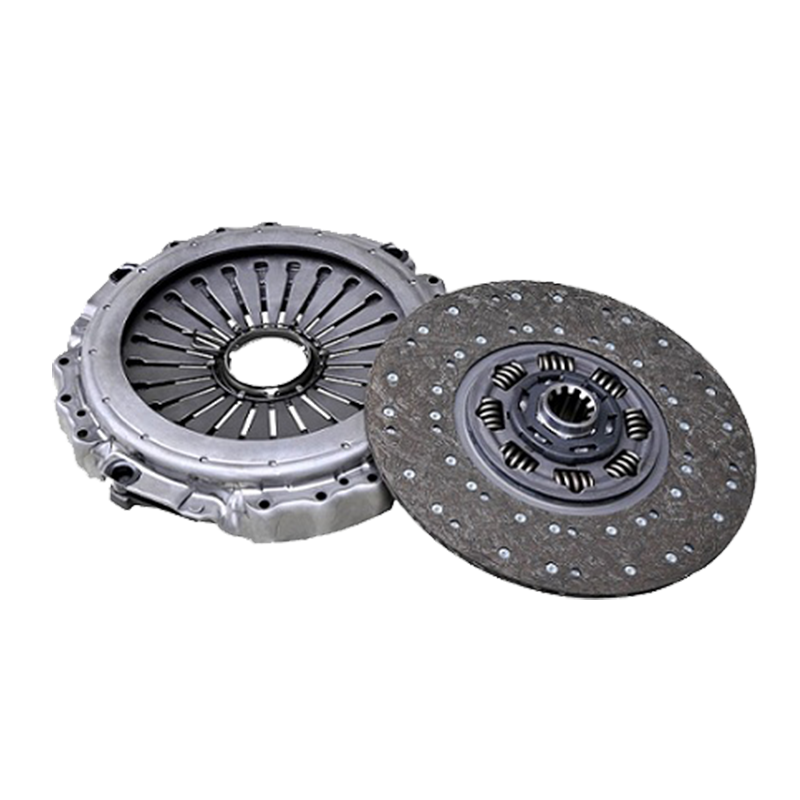
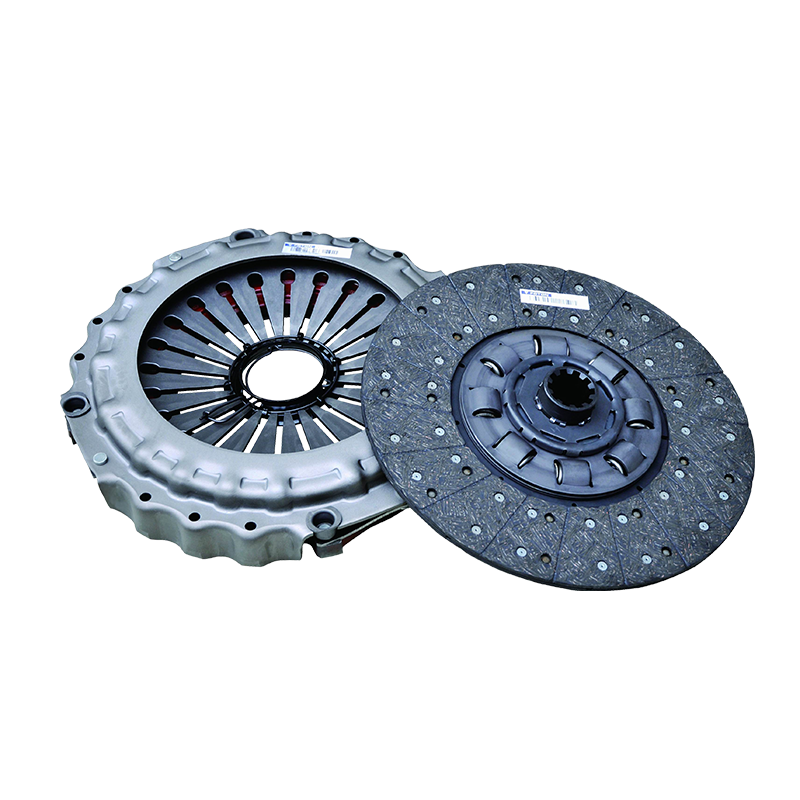
In order to further improve the heat dissipation efficiency, the 430 push clutch assembly also adopts a variety of heat dissipation optimization designs. A common way is to design heat sinks on the outside of the assembly. These heat sinks effectively improve the heat dissipation efficiency by increasing the surface area, and can transfer heat from the inside of the clutch to the outside air faster to prevent the internal temperature from being too high.
In addition, the 430 push clutch may also be equipped with an air cooling device. In a high temperature or high load working environment, the air cooling device can introduce cold air from the outside into the clutch by forced convection, accelerate the loss of heat, and further reduce the working temperature of the clutch. These designs not only extend the service life of the clutch, but also improve the operating efficiency of the overall system.
The impact of thermal management on performance
In the actual use of clutch components, thermal management is one of the key factors affecting their performance. By optimizing the heat dissipation design and using high temperature resistant materials, the 430 push clutch can not only maintain stable operation for a long time in a high temperature environment, but also reduce the risk of failure caused by thermal decay of the friction plate material. This allows it to maintain excellent performance under long-term high load conditions.
 English
English русский
русский




 English
English  No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.
No.25, Hu Chuang Road, New District Industrial Park, Suzhou, Jiangsu, China.  +86-13338663262
+86-13338663262 
